El libro negro de los colores (2006)
The Black Book of Colors (2009)
Menena Cottin and Rosana Faría
Dustjacket, casebound, black doublures, sewn. H180 x W290, 24 unnumbered pages. Acquired 17 October 2017.
Photos: Books On Books Collection. Displayed with author’s permission.
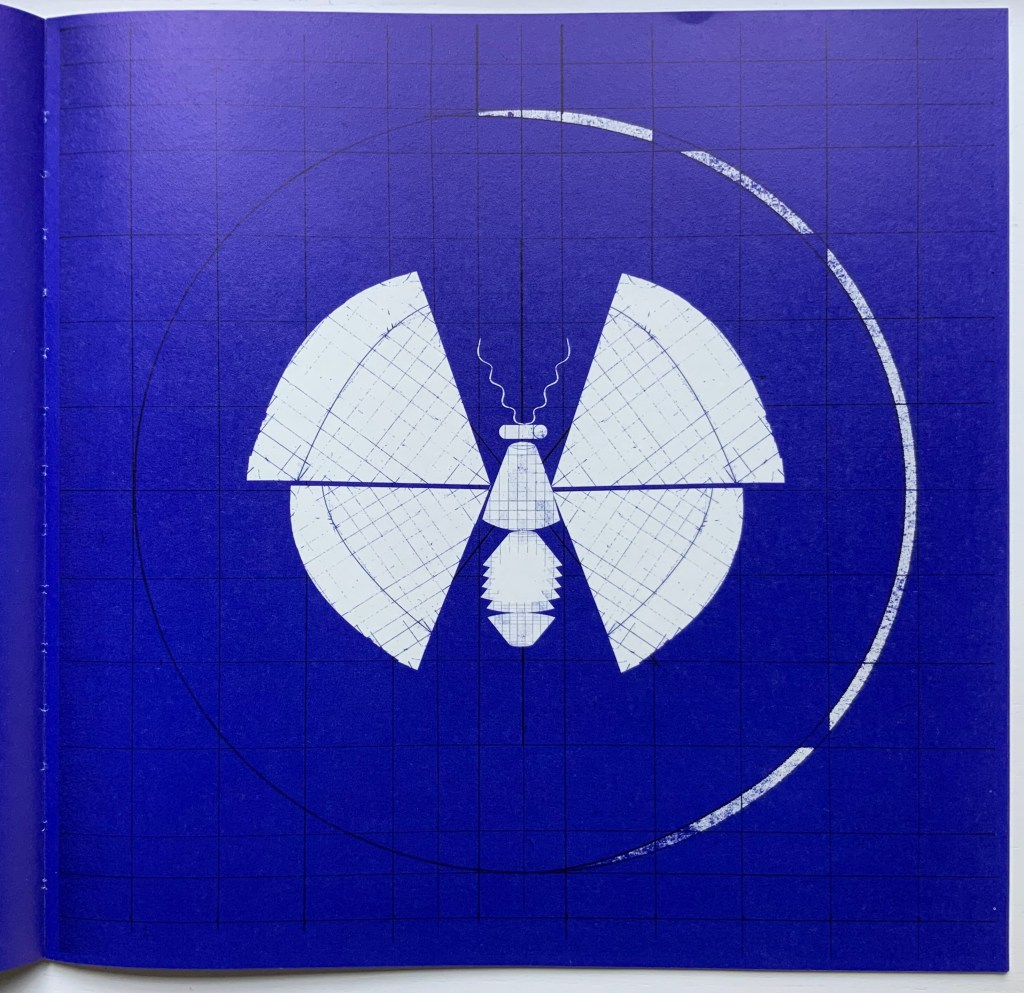
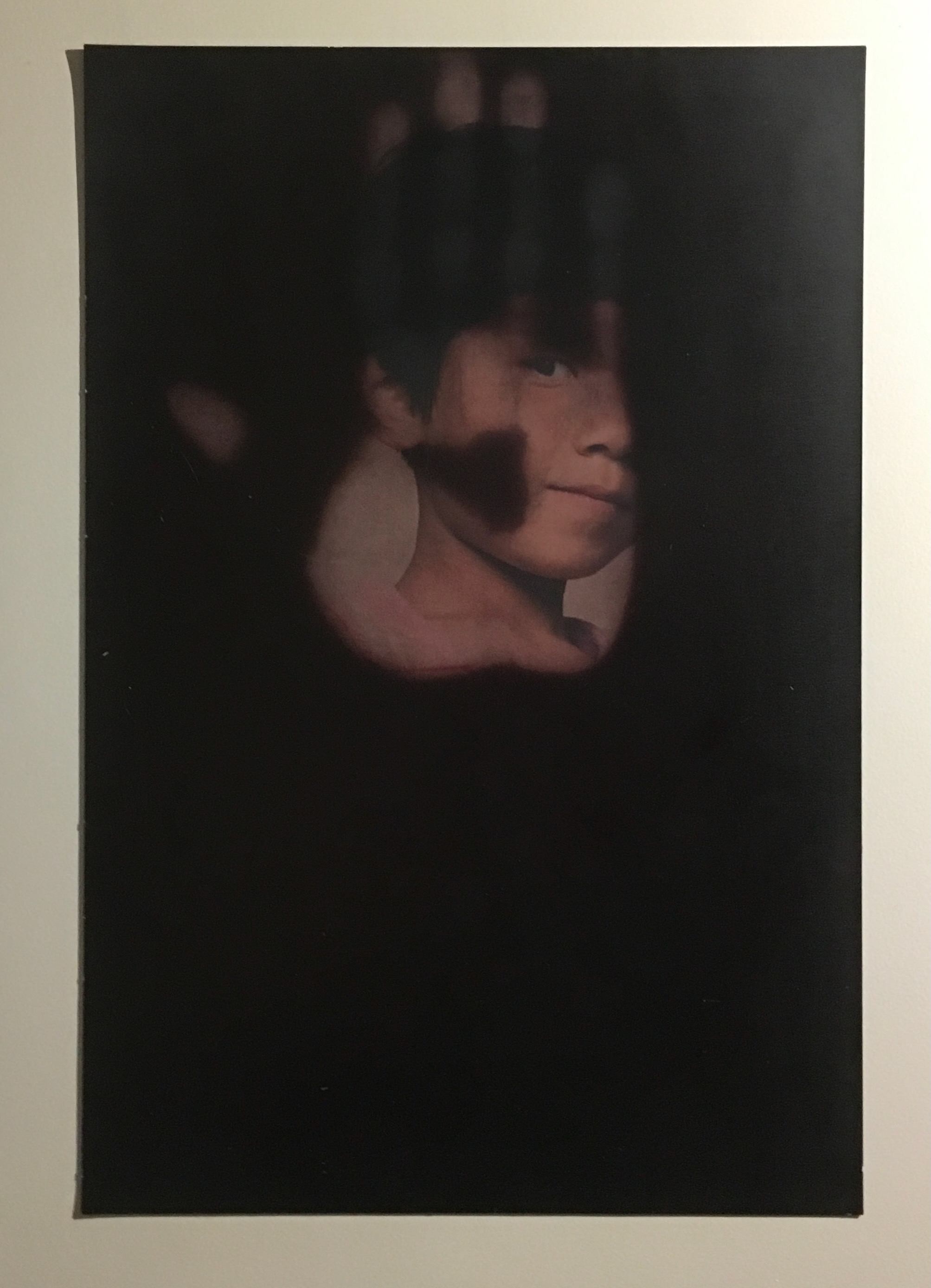
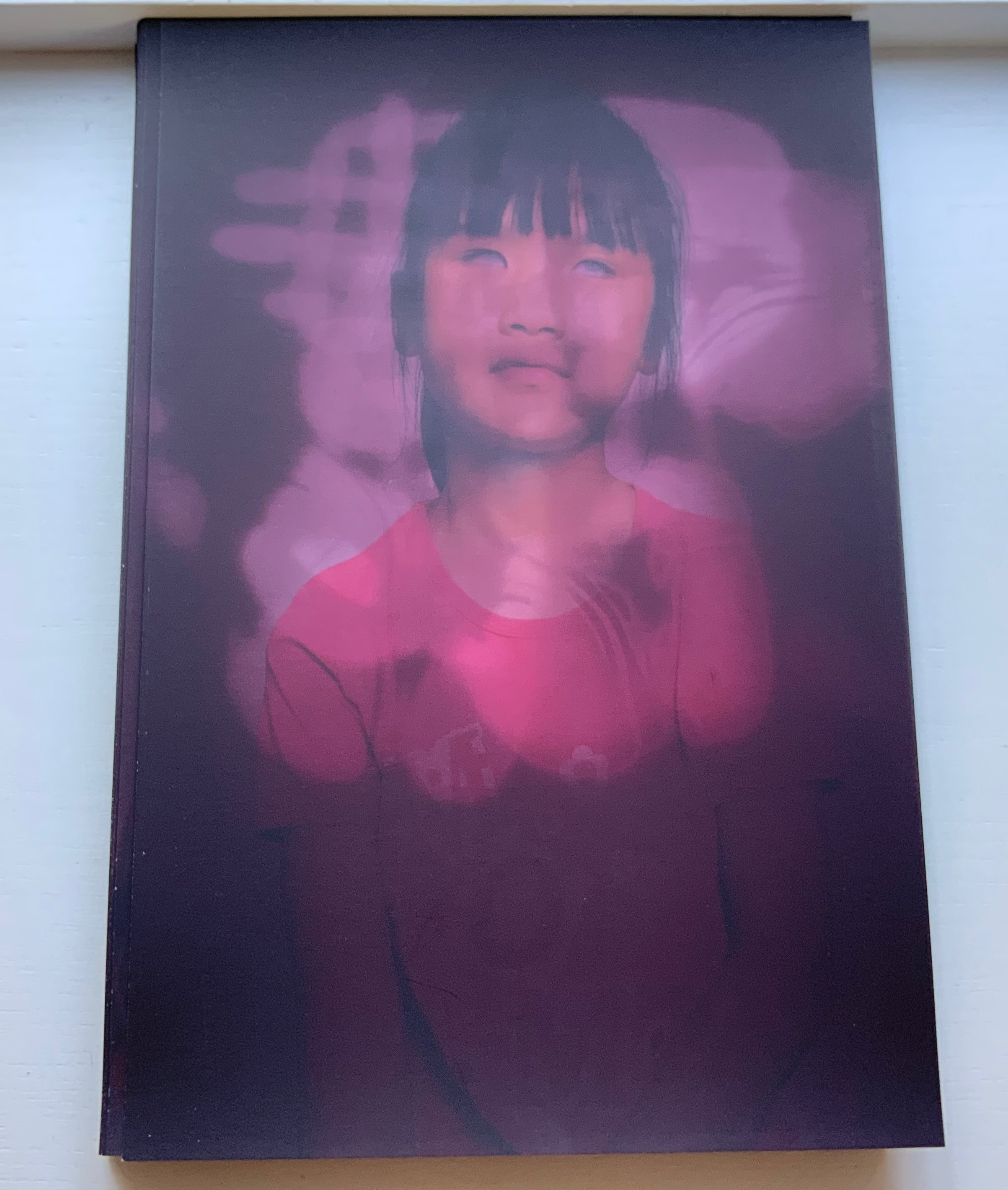
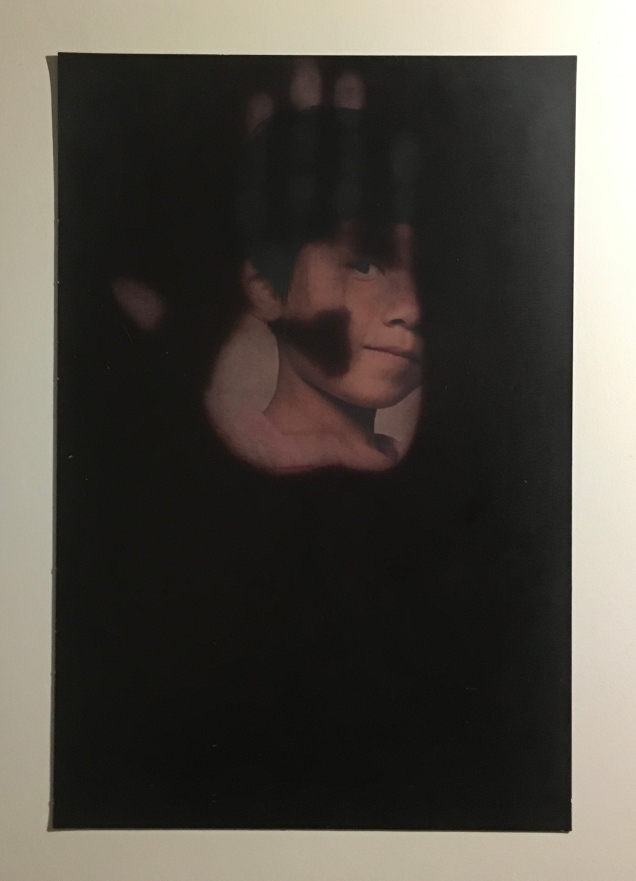
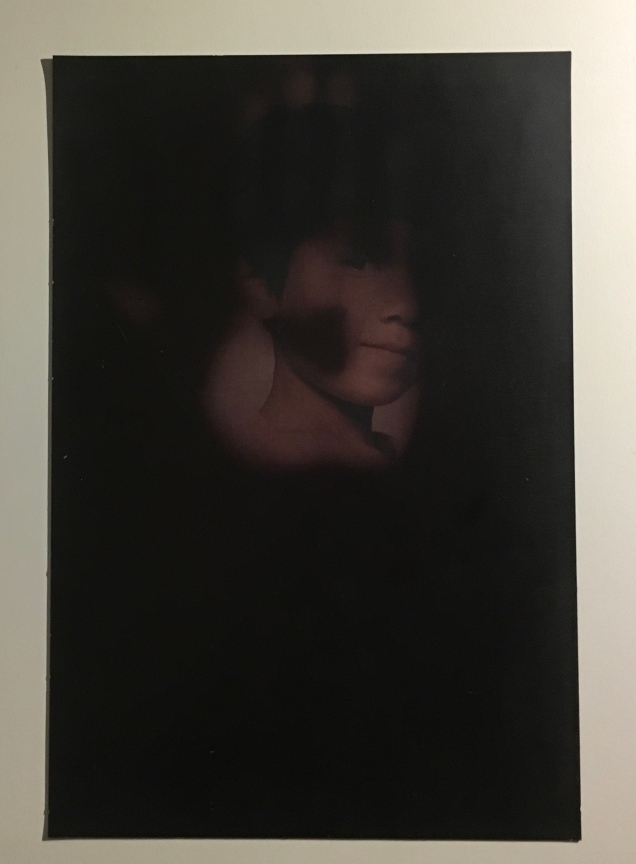
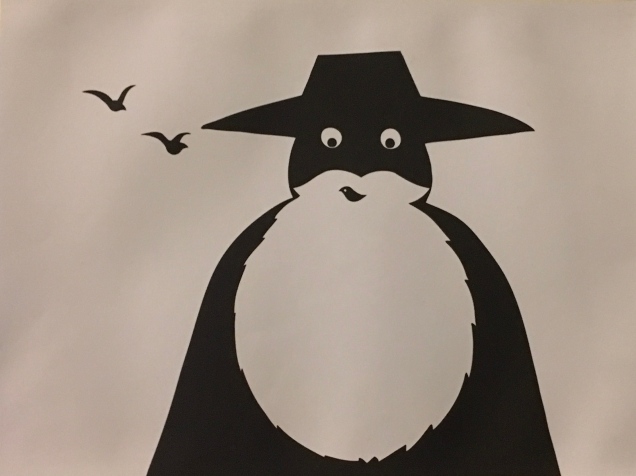
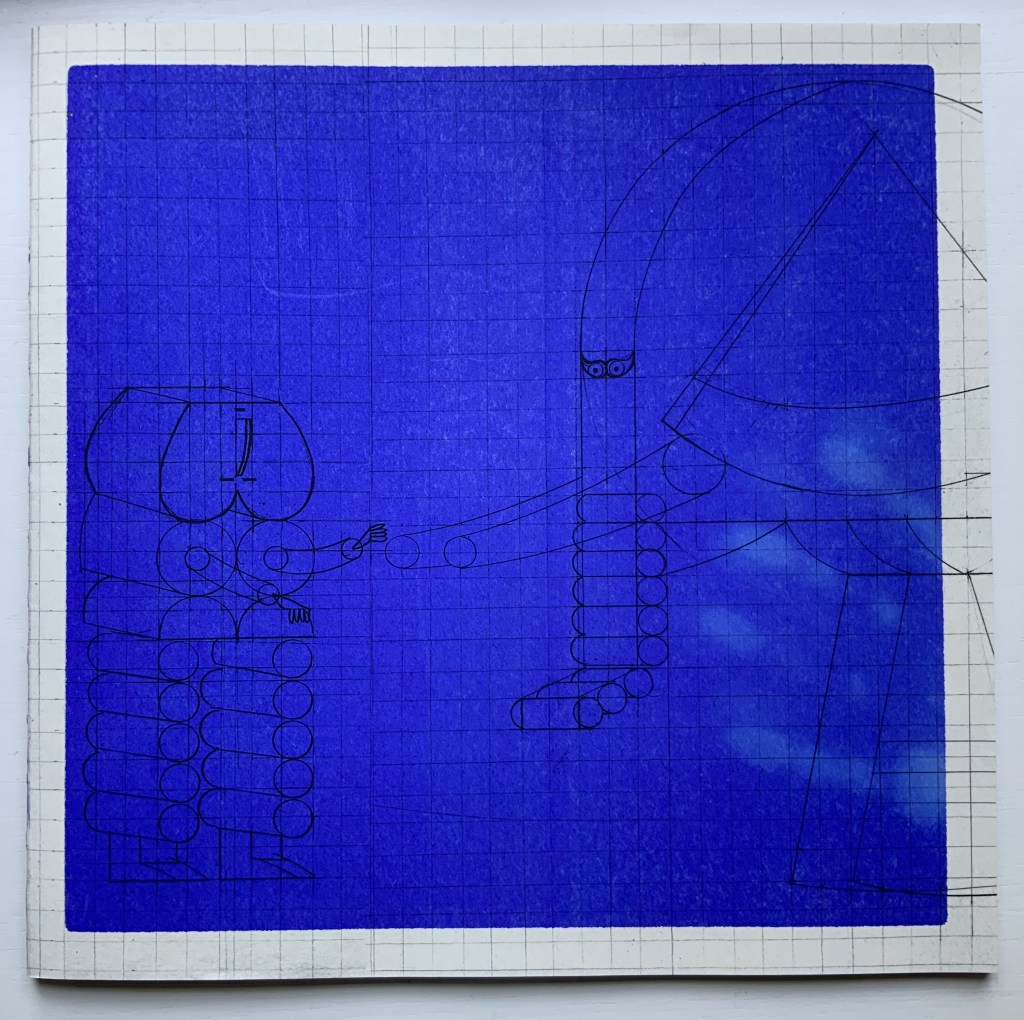
Menena Cottin refers to her works as “concept books”, and there are multiple concepts at work in The Black Book of Colors. Generically, it is a children’s book introducing the reader to colors — but by the absence of color. In white on black, it addresses sighted readers. In Braille, it addresses unsighted readers. With Thomas, who “likes all the colors because he can hear them and smell them and touch and taste them”, the book introduces to sighted and unsighted readers who are not synesthetic the concept of synesthesia and, through it, a new sense of empathy and imagination. The sighted encounter someone with a sensory anomaly, not a disadvantage. In the company of their imagined unsighted co-readers, the sighted may come to empathize with those with sensory differences. The unsighted encounter someone whose sensory anomaly is an advantage. especially as the book favors their own heightened sense of touch.

Thomas says that yellow tastes like mustard, but is as soft as a baby chick’s feathers.

Thomas likes all the colors because he can hear them and smell them and touch and taste them.
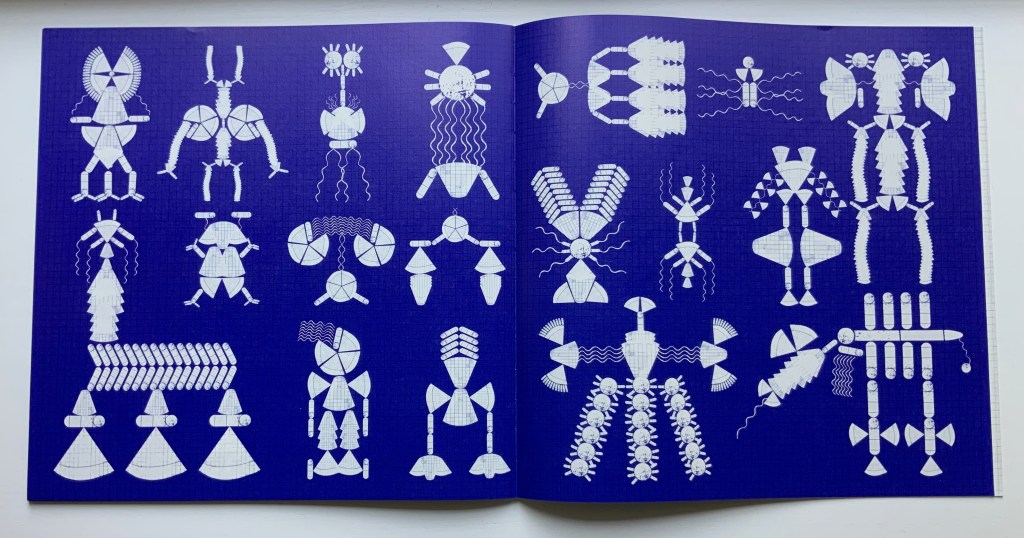
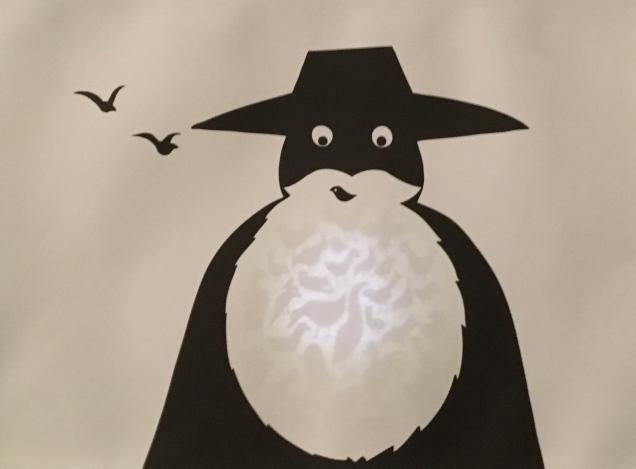
Breaking boundaries in ways similar to those employed by book artists, Cottin manipulates character and narration, also the picturebook’s genres of color recognition and letter recognition (Braille in this case) as well as some of the basic elements of the book (layout, printing in reverse-out and debossed printing). In one of the most sophisticated examples of this, double-page spreads fuse concepts by turning a rainbow into a gathering of raised images of the synaesthetic objects with which colors have already been associated in the book (chick’s feathers, strawberries, leaves).

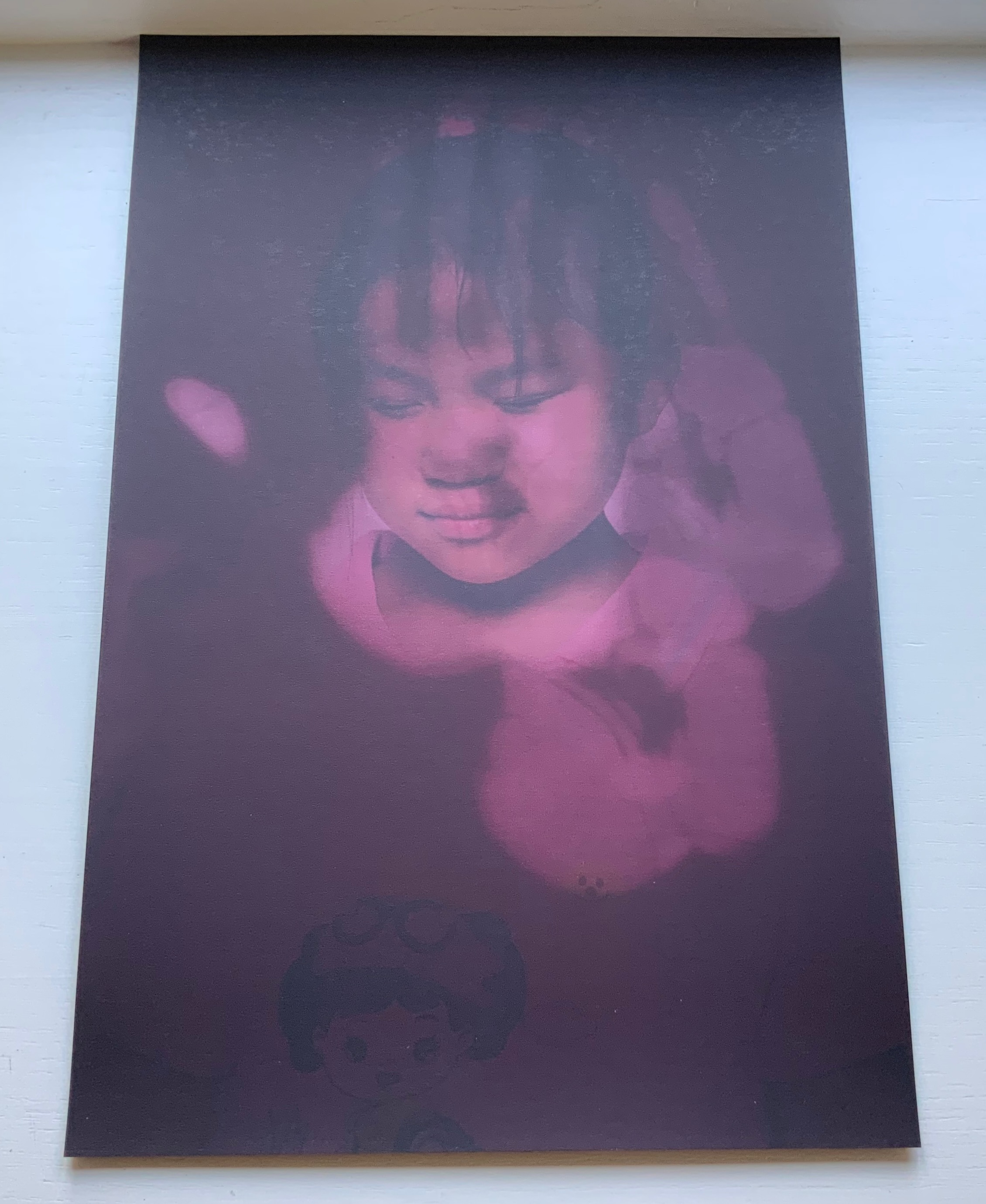
And when the sun peeks through the falling water, all the colors come out, and that’s a rainbow.
The Black Book uses synesthesia to go beyond the color recognition genre to introduce more complex concepts: the nature of light and water’s lack of color, taste and smell. This stepping outside the genre is another example of the boundary-breaking that artists’ books often perform.

Thomas thinks that without the sun, water doesn’t amount to much. It has no color, no taste, no smell.
The book ends by asserting its membership in the alphabet book genre by presenting the alphabet in lowercase white on black and in Braille. Across from this verso page, there is no set of raised images on the recto page as there has been so far throughout the book. Knowing from touch that this is the end of the book and noting the absence of any image, sighted and unsighted readers might find this coda a prompt to return to the beginning and “re-read” the images with a greater reliance on touch.

Other books in the Books On Books Collection worth comparing with The Black Book of Colors are
Like a Pearl in My Hand (2016) Carina Hesper
Vladimir Nabokov: AlphaBet in Color (2005) Jean Holabird
Blindness (2020) Masoumeh Mohtadi
Voyelles (2012) Arthur Rimbaud/Le Cadratin
Darkness Visible (2017) Sam Winston
The Blind Men and the Elephant (2019) Xiao Long Hua
La Doble Historia de un Vaso de Leche (2019)


La Doble Historia de un Vaso de Leche (2019)
Menena Cottin
Casebound landscape, paper over boards, with orange-yellow doublures, sewn. H160 x W310 mm. 24 unnumbered pages. Acquired from the artist, 2022.
Photos: Books On Books Collection.
The Double Story of a Glass of Milk opens and closes with a line that echoes the start of William Carlos Williams’ “The Red Wheelbarrow” but is at once more straightforward and just as surprising — as the visual story spills out.
Todo depende del ángulo en que lo miras. A veces un cuadrado puede también ser un circulo y una larga linéa luce como un punto y algo que está solo a medias parece que está lleno. Un mismo cuerpo tiene diferentes caras per a veces te confunde mostrándote una misma forma. Solo si miras a su alrededor descubres que … eso que de frente parece tan discreto desde arriba luce muy escandaloso. Todo depende del ángulo en que lo miras.
“Everything depends on the angle from which you look at it. Sometimes a square can also be a circle and a long line looks like a dot and something only half full looks full. The same body has different faces but sometimes it confuses you by showing you a different shape. Only if you look you discover that … what from the side looks so innocent looks shocking from above. Everything depends on the angle from which you look at it.”


Equilibrio (2019)


Equilibrio (2019)
Menena Cottin
Casebound landscape, paper over boards, with red doublures, sewn. H160 x W310 mm. 25 unnumbered pages, last page on inside of flyleaf. Acquired from the artist, 23 August 2022.
Photos: Books On Books Collection. Displayed with the author’s permission.
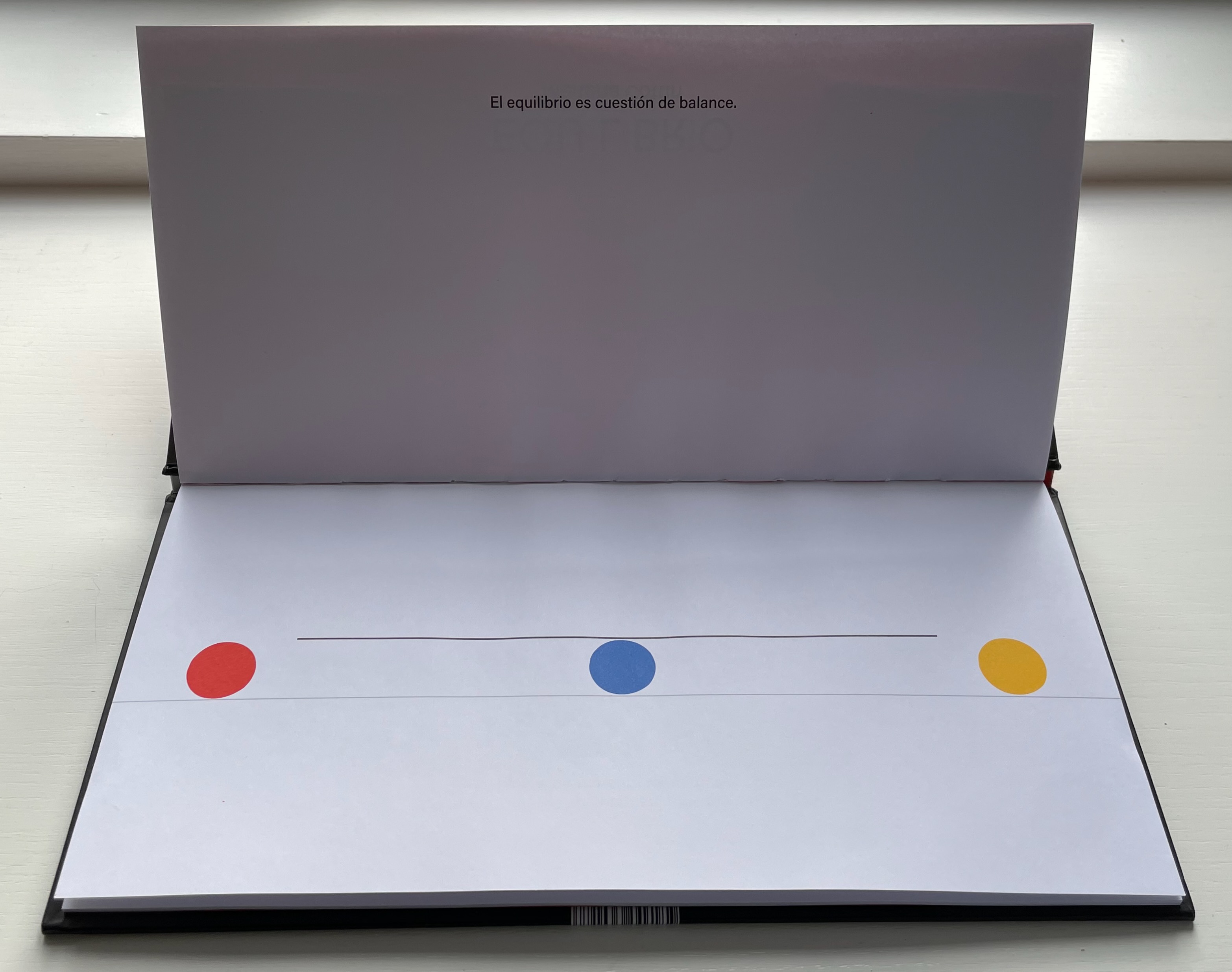
The three colored balls on the cover give their colors to the three i’s in Equilibrio on the title page, announcing the statement to come: El equilibrio es cuestión de balance (“Equilibrium is a question of balance”).
El equilibrio es cuestión de balance. De tomar siempre en cuenta el movimiento del otro y reaccionar para mantenerlo, calculando, arriesgando, y experimentado. Algunos se ponen a jugar sin pensar en las consecuencias entonces se rompe el equilibrio y cada quien hace lo que quiere … pero luego sienten deseos de regresar y cada quien busca su lugar.
“Equilbrium is a question of balance. Of always taking into account the movement of the other and reacting to maintain it, calculating, risking, and experimenting. Some people start to play without thinking about the consequences, then the balance is broken and everyone does what they want … but then they feel the desire to return and everyone looks for their place.”.
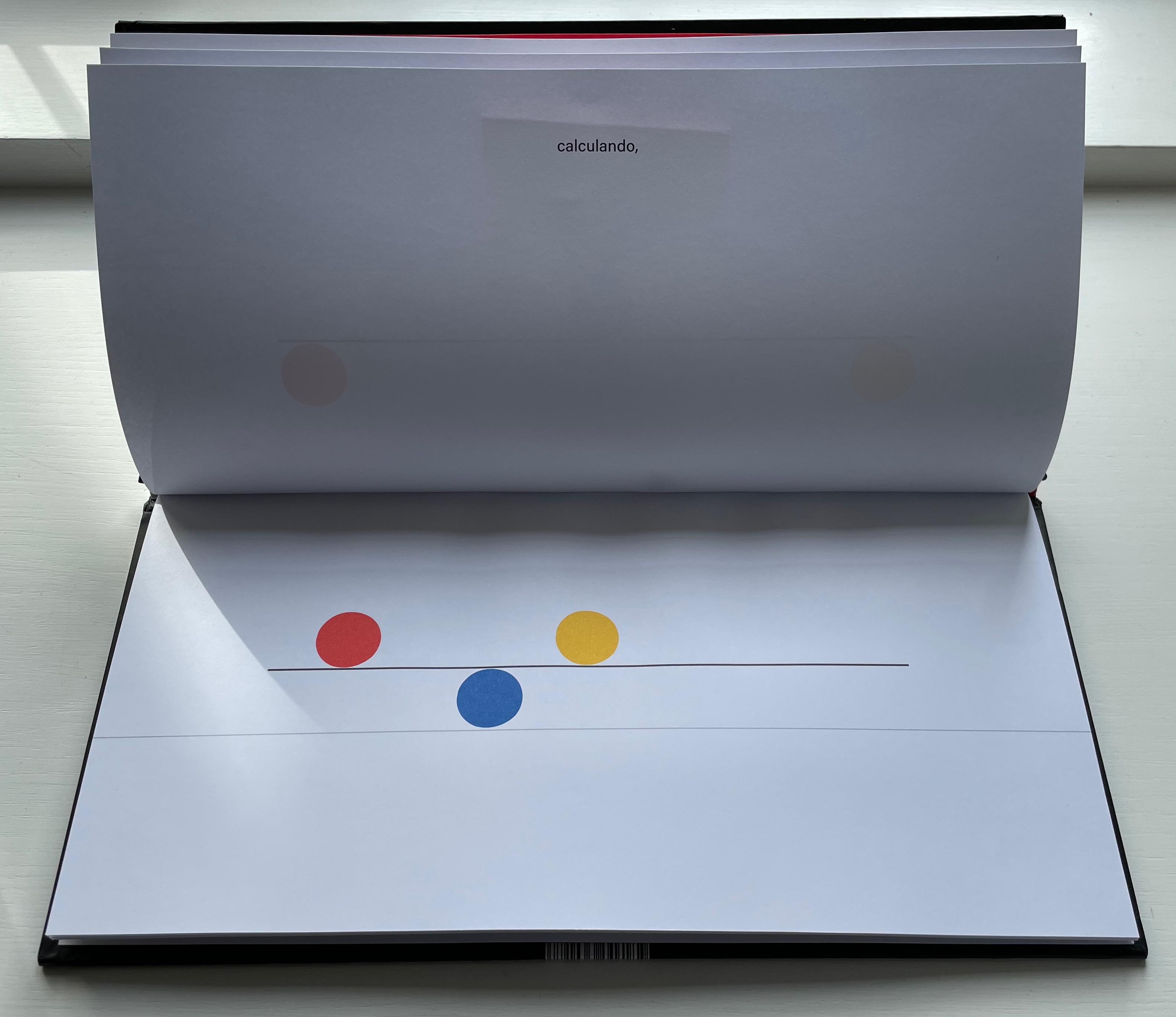
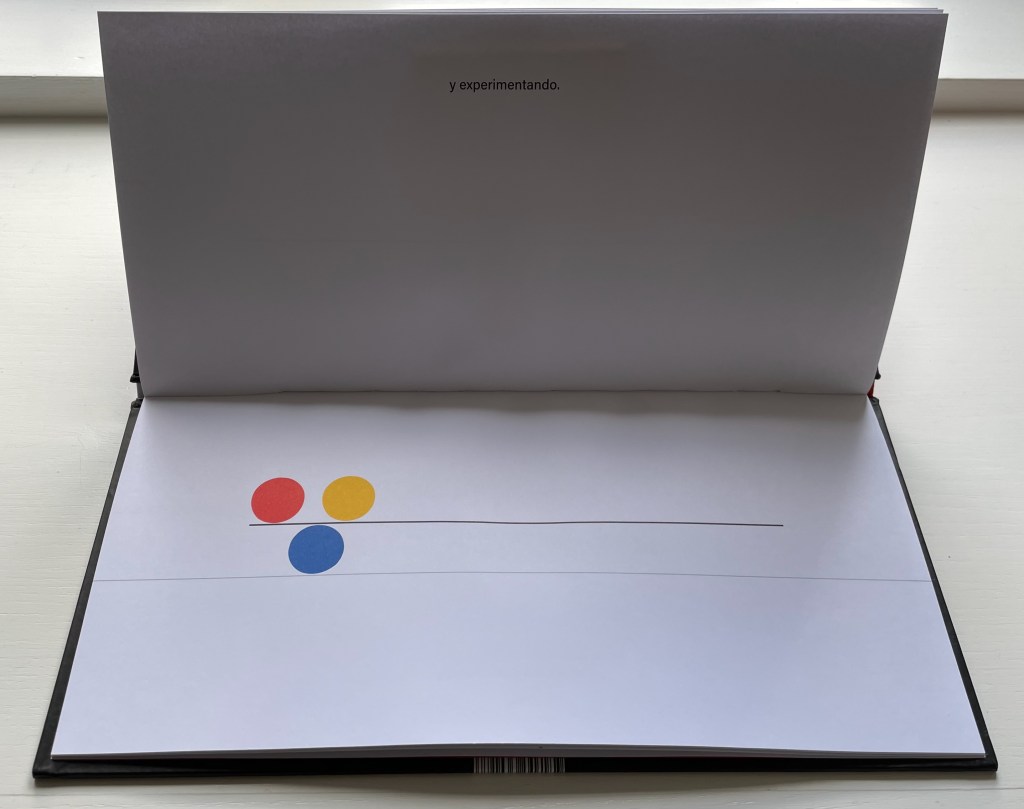





As in The Black Book of Colors, there is more than one concept at play, the lesson of equilibrium coming with lessons in community and relationships.
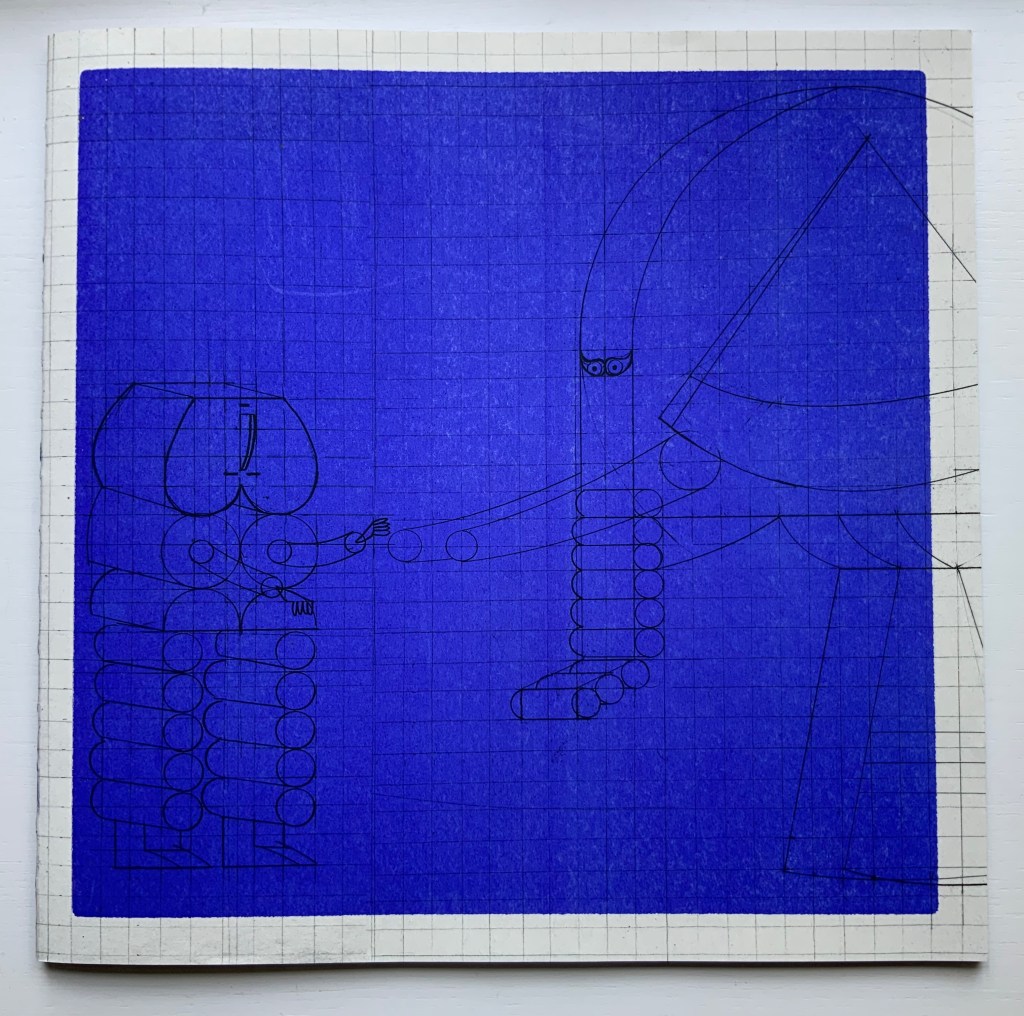
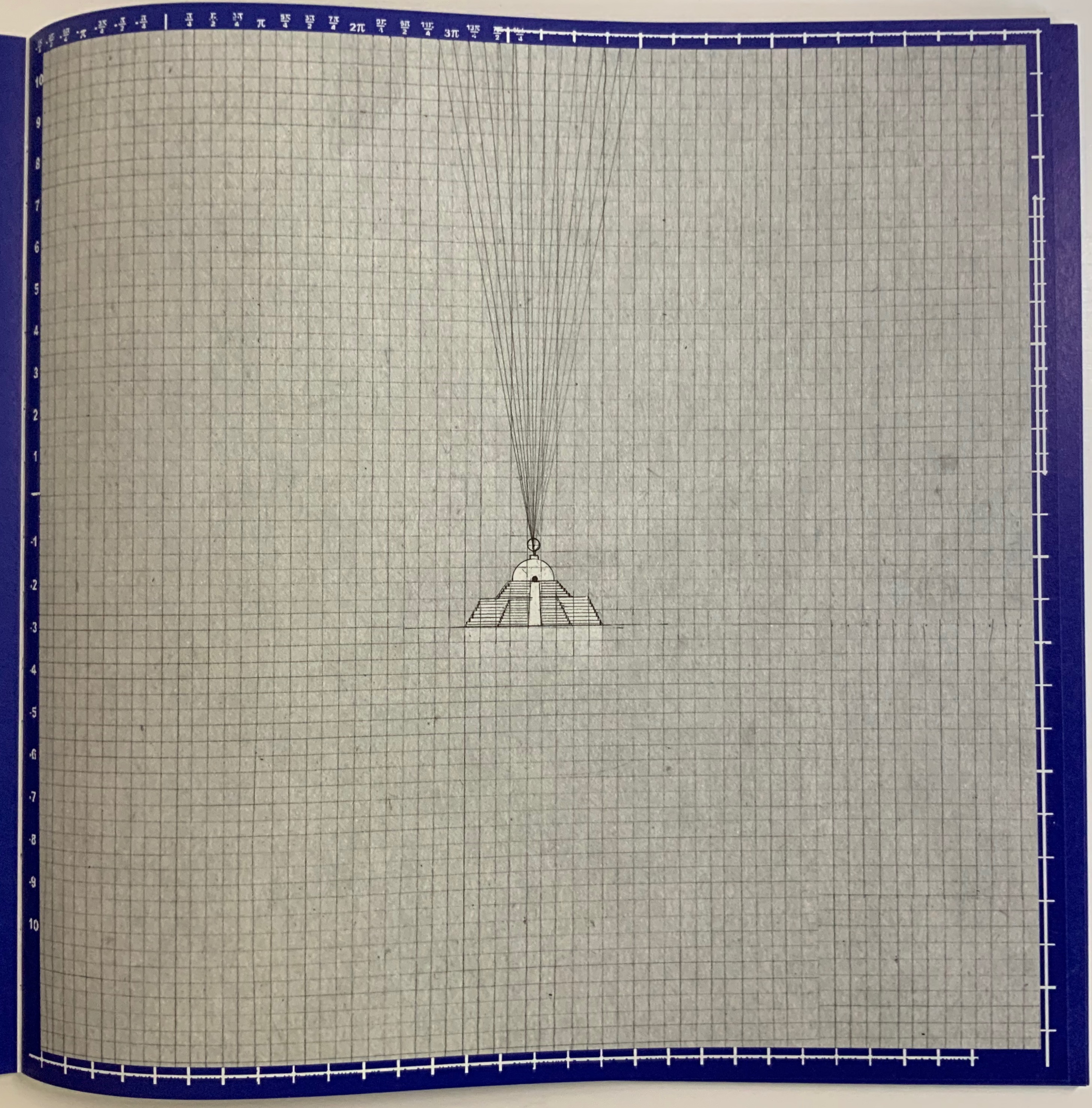
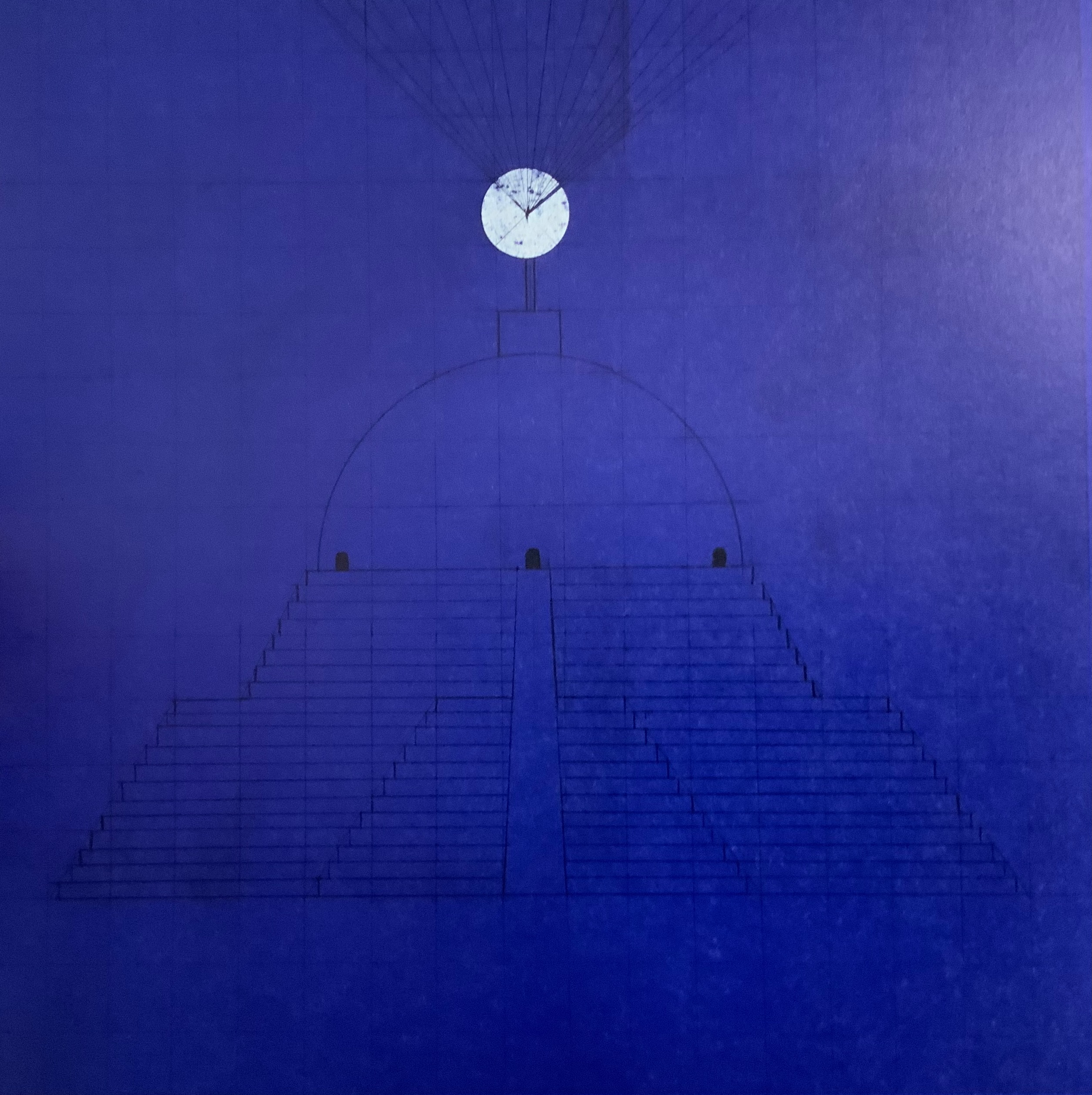
El Tiempo (2018)

El Tiempo (2018)
Menena Cottin
Casebound portrait, paper over boards, with orange-yellow doublure at front, orange-yellow/black at back, sewn. H310 x W160 mm. 24 unnumbered pages. Acquired from the artist, 23 August 2022.
Photos: Books On Books Collection. Displayed with author’s permission.
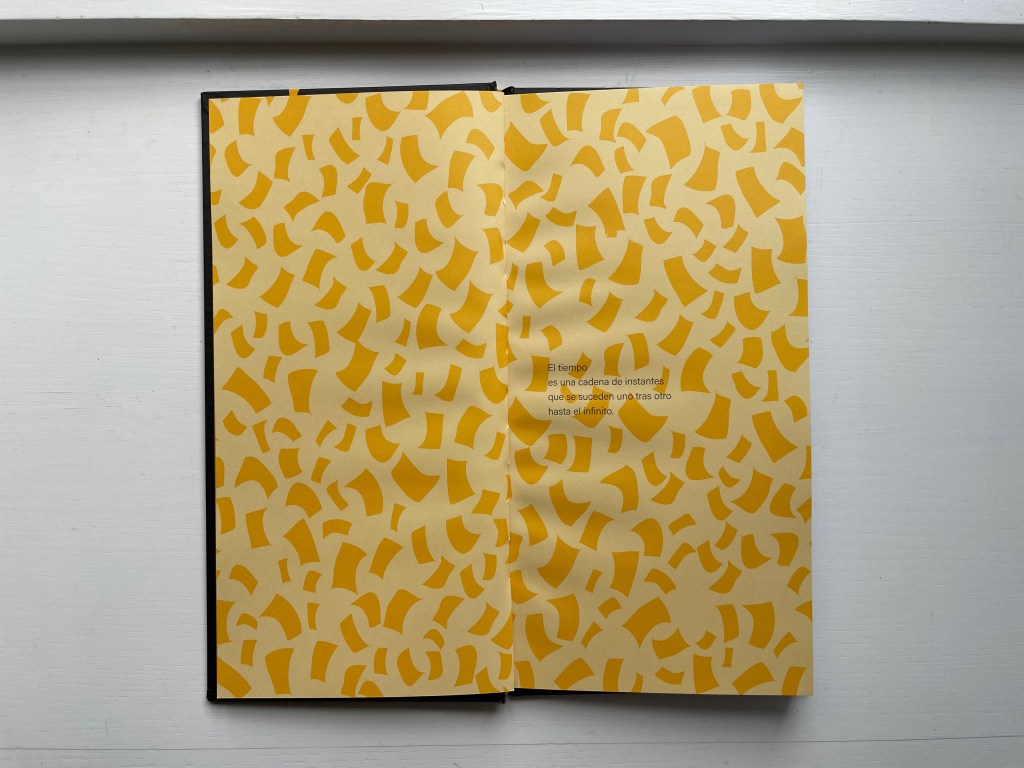
Cottin introduces the concept of Time with two metaphors — one verbal, one visual.
Verbally: El tiempo es una cadena de instantes que se suceden uno tras otro hasta el infinito. [Time is a chain of instants one following another until infinity.] Visually: Instants of time are like pages, pages from a diary.


Even in an hour glass, the instants of time are golden pages — Se divide en pasado, presente y futuro que es lo mismo que antes, ahora y después. — [dividing the past, present and future which is the same as before, now and after].

When the future runs out, that is of course when the pages run out, visually and tactilely.
Ana con A, Otto con O (2015)
Ana con A, Otto con O (2015) [Ana with an A, Otto with an O]
Menena Cottin
Bradel binding with cloth spine, paper over boards, yellow doublures, leaves in Chinese fold. H85 x W260 mm. 42 unnumbered pages. Acquired from the artist, 23 August 2022.
Photos: Books On Books Collection. Displayed with author’s permission.
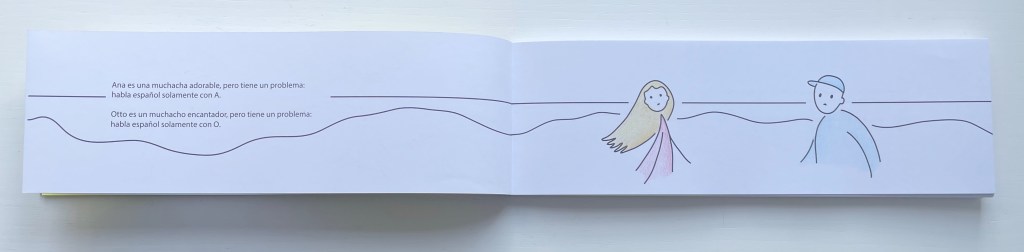
With this little book, Menena Cottin has secured a place among the Oulipians. Where Georges Perec wrote a novel without the letter E, Cottin has written and created an artist’s book in which the characters have a somewhat opposite challenge.
Ana es una muchacha adorable, pero tiene un problema: habla español solamente con A. Otto es un muchacho encantado, pero tiene un problema: habla español solamente con O. Un domingo por la mañana, en isla de Margarita, Ana sale a caminar por la playa. Otto sale a caminar por la playa. De repente, Ana se tropieza con alguien …
–Aah!
–Oh!
[Ana is a lovely girl, but she has a problem: she speaks Spanish only with words that have an A. Otto is a lovely boy, but he has a problem: he speaks Spanish only with words that have an O. One Sunday morning, on Margarita Island, Ana goes for a walk on the beach. Otto goes for a walk on the beach. Suddenly, Ana bumps into someone …
–Aah!
–Oh!]
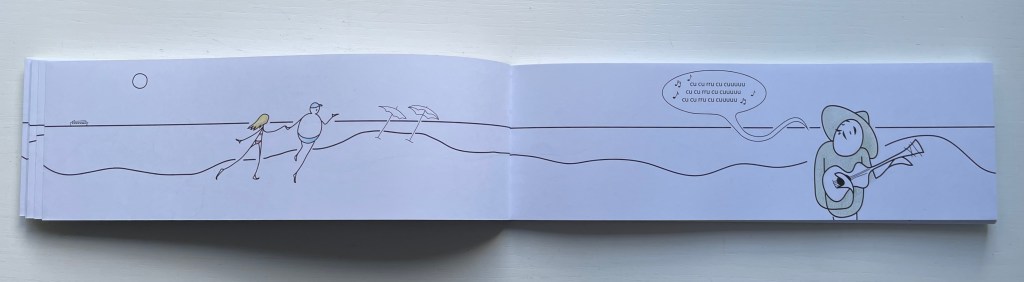
When they make small talk about the weather, Ana says, Clara mañana [Clear tomorrow] with which Otto agrees, Con sol [With sun]. Ana tries again with a leading Gran playa, la mar calmada … agradar andar acá. [Great beach, calm sea… it’s nice to walk here.], but Otto can only come up with ¡Como, no! [Of course!].
Eventually Otto catches on and proposes they go for a swim. After, as they walk along the beach being serenaded by a guitar-playing singer whose nonsense refrain is with syllables that have only U, Otto invites Ana to lunch at the beachside restaurant El Pez [The Fish]. There they meet the friendly waiter Pepe, who likewise has a problem: he speaks Spanish only with words that have an E. When their meal ends and Otto sees the bill, he grows pale, suspiciously throws himself to the ground, cries out he’s been poisoned, and then runs off with Pepe in pursuit of payment. Poor Ana wanders back down the beach, but bumps into another character, more handsomely drawn and simpatico: Allan with an A. Colorín colorado, as the Spanish say [And that’s the end of this story], but not until the last page where the character who has been lounging in a beach chair all along now stands, revealing her name on her chair — Iris — and holding a sign that reads Fin.
The rule-abiding dialogue strings the reader along as effectively as the horizon line that runs from page to page over the Chinese folded folios from the beginning to the end. It is a design feature that will be much easier to reproduce than will a translation into English or any other non-Romance language that is as delightful as — or as “consonant” with — Ana, Pepe, Iris, Otto and the singer singing
Las Letras (2008/2018)

Las Letras (2018) [Letters]
Menena Cottin
Casebound portrait, illustrated paper over boards, endpapers. H200 x W205 mm. 24 unnumbered. Acquired from the artist, 23 August 2022.
Photos: Books On Books Collection. Displayed with author’s permission.
Las Letras has appeared in two editions (2008 and 2018). There are slight grammatical differences, but the meaning remains unchanged. As in Equilbrio, where Cottin finds in an abstract concept a metaphor for interdependence in human relationships, in Las Letras Cottin finds a metaphor for tolerance and communication in the alphabet. Even letters themselves celebrate our differences.
Las personas son como las letras, cada una es diferente a la otra, con su propia forma, su propia forma, su propia voz y su personalidad. Pueden ser gordas, flacas, sencillas o complicados. Algunas son muy populares y se les ve por todas partes, en cambio, a las más tímidas les gusta salir poco. …
[People are like letters, each one is different from the other, with its own form, its own shape, its own voice and its own personality. They can be fat, skinny, simple or complicated. Some are very popular and are seen everywhere, while the shyer ones don’t like to go out much. …]


Other children’s/artists’ books in the Books On Books Collection worth comparing with Las Letras are:
Dessine-moi une lettre (2004) Anne Bertier
A is for Bee (2022) Ellen Heck
One & Everything (2022) Sam Winston
Further Reading
“Abecedaries I (in progress)“. Books On Books Collection.
Beckett Sandra L. 2013. Crossover Picturebooks : A Genre for All Ages. London: Routledge.
Cave Roderick and Sara Ayad. 2017. A History of Children’s Books in 100 Books. London: British Library Publishing Division, pp. 26-27.
Nikolajeva, Maria, and Carole Scott. 2007. How picturebooks work. New York: Routledge Taylor & Francis Group.
Outlaw, Christopher. 17 April 2017. “FILBo 2017“. The Bogotá Post. Accessed 30 October 2011.
Scott, Carole. 2014. “Artists’ books, Altered books, and Picturebooks”. In: B. Kümmerling‐Meibauer, ed., Picturebooks: Representation and Narration. London, New York: Routledge.