The [artists’ book] movement had its beginnings with a few individuals (conceptual artists Dieter Roth, Hansjörg Mayer, and Ed Ruscha immediately come to mind), but in the area of structural experiment and invention only one person seems to have been markedly influential (albeit seriously ignored): Hedi Kyle.
Alastair Johnston, “Visible Shivers Running Down My Spine”, Parenthesis, Fall 2013, Number 25.
While Alastair Johnston’s 2013 interview with Hedi Kyle is a rich one and welcome, it is inaccurate to say Hedi Kyle has been seriously ignored. After all, in 2005, the Guild of Book Workers awarded her an honorary membership, and Syracuse University’s Library invited her to deliver that year’s Brodsky Series lecture. In 2008, the Philadelphia Senior Artists Initiative recorded her oral history and posted her artist’s statement along with an extensive list of prior exhibitions, honors, professional roles and board memberships stretching back to 1965.
If, however, Johnston’s assessment is accurate, subsequent events have rectified the situation. In 2015, Kyle delivered the keynote address “Four Decades under the Spell of the Book” for the Focus on Book Arts annual conference. In the same year, the 23 Sandy Gallery held a successful international juried exhibition entitled “Hello Hedi“, an echo of the 1993 exhibition organized by the New York Center for Book Arts entitled Hedi Kyle and Her Influence, 1973-1993. In 2016, the San Francisco Center for the Book held a solo exhibition for Kyle: “The World of Hedi Kyle: Codex Curios and Bibli’objets“.
And now, in 2018, Laurence King Publishers has brought out the eagerly awaited The Art of the Fold by Kyle and daughter Ulla Warchol, which is the immediate impetus for this essay. The authors aim their book at artists and craftworkers, but there is a secondary audience: anyone interested in book art or artists’ books or origami — and learning how better to appreciate them.
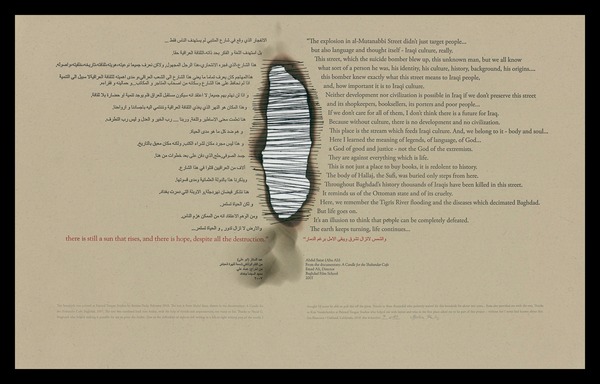
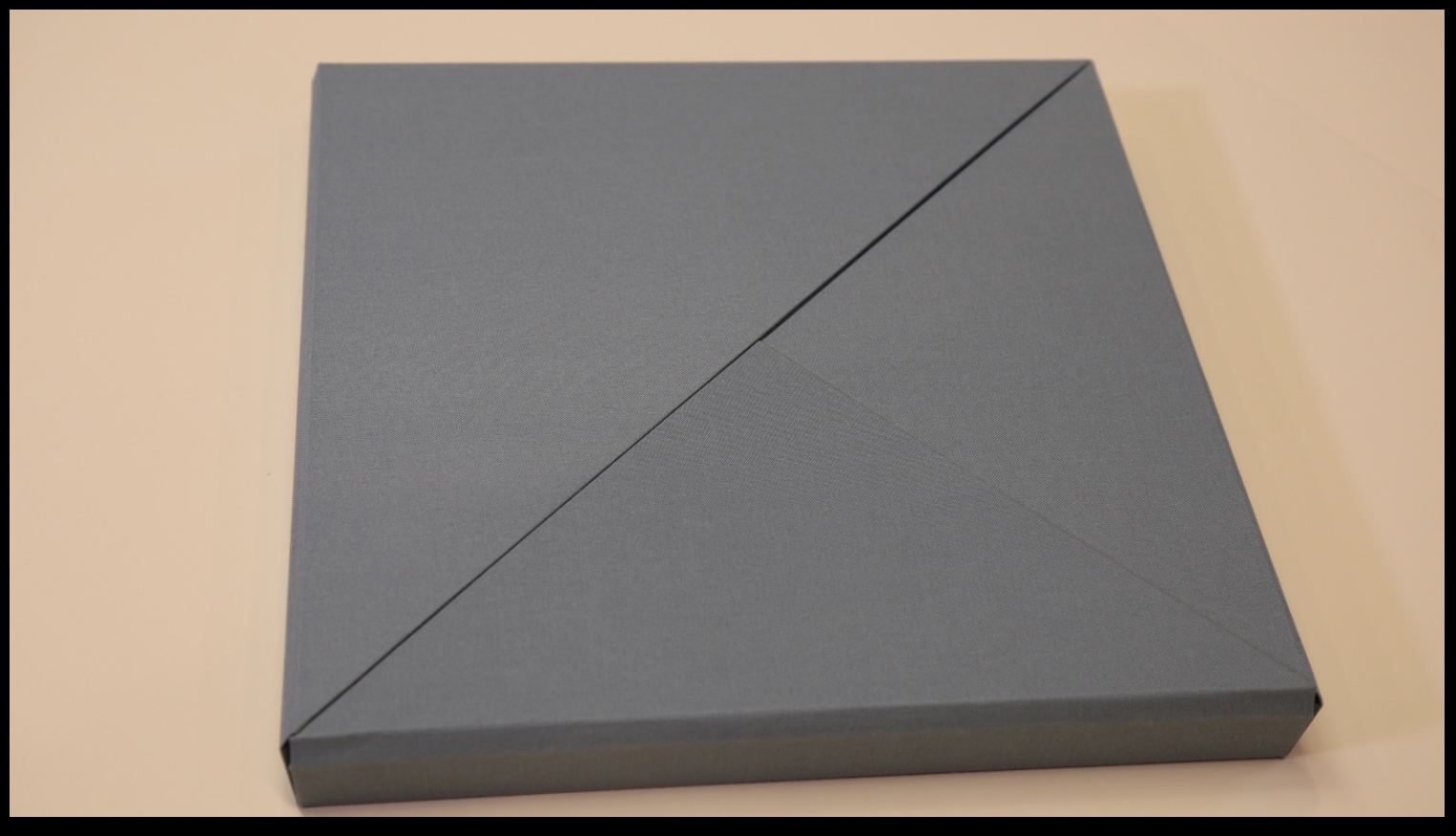
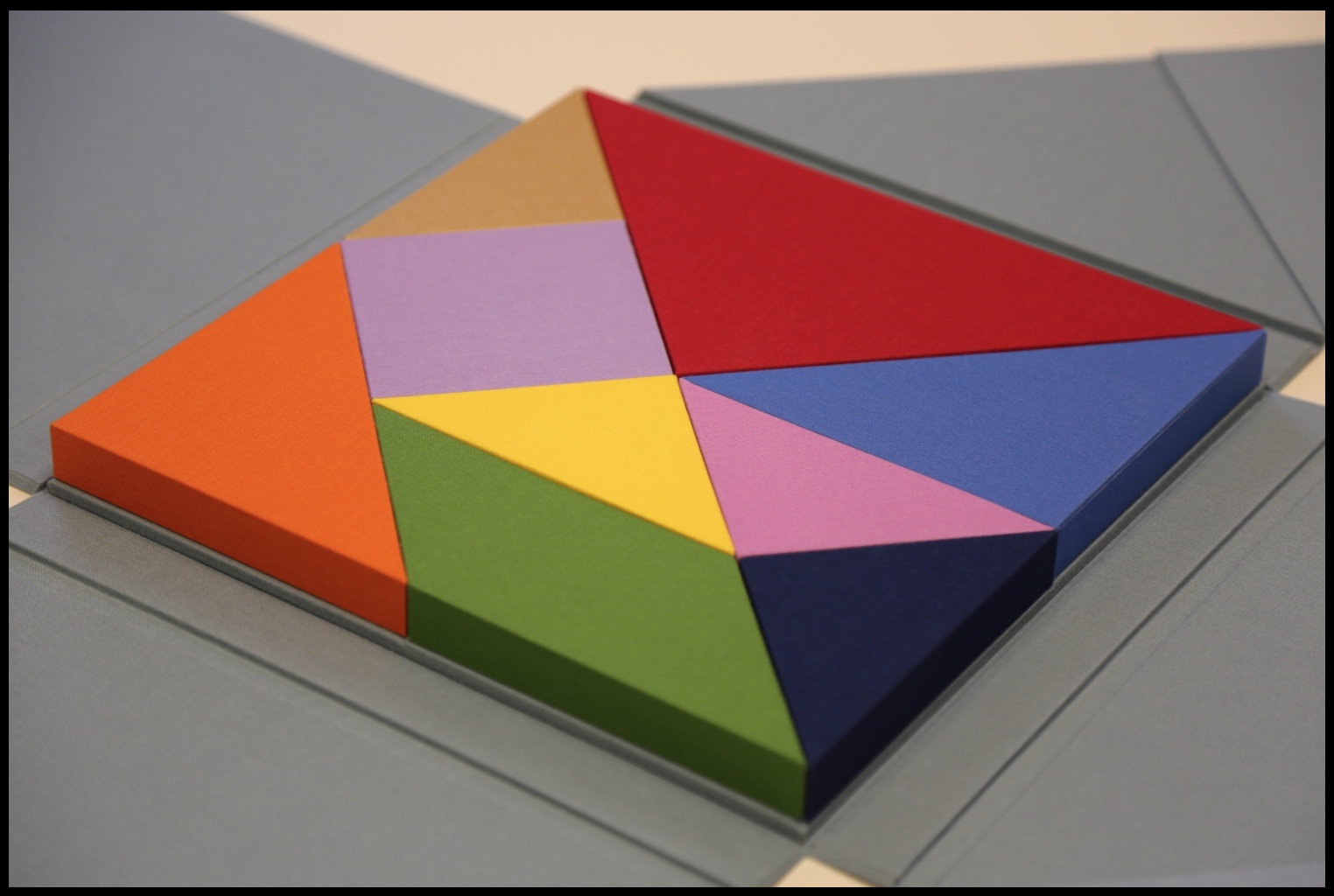
On picking up the book, the first thing its primary and secondary audiences should notice is the folded “dust jacket”. Why the quotation marks? Just look:




“Dust jacket” unfolded, side 1

“Dust jacket” unfolded, side 2
This innovative, subject-appropriate cut, fold and print can set the reader on a hunt for precursors such as Peter and Pat Gentenaar-Torley’s Paper Takes Flight/Papier op de Vlucht, designed by Loes Schepens, where the multilayered dust jacket has small envelopes attached to hold paper samples from the contributing artists, or Doug Beube’s Breaking the Codex, designed by Linda Florio, where the dust jacket includes a perforated bookmark, whose removal implicates the reader in a bit of biblioclasm and challenges Western parochialism.

Paper Takes Flight/Papier op de Vlucht (2006) Peter and Pat Gentenaar-Torley Note how the book’s title is revealed on the second dust jacket from the bottom.

The five opened dust jackets displayed beneath the title page

Bottom-most dust jacket folded from the backboard to the right revealing the airmail envelope, which contains a blank sheet of airmail stationery
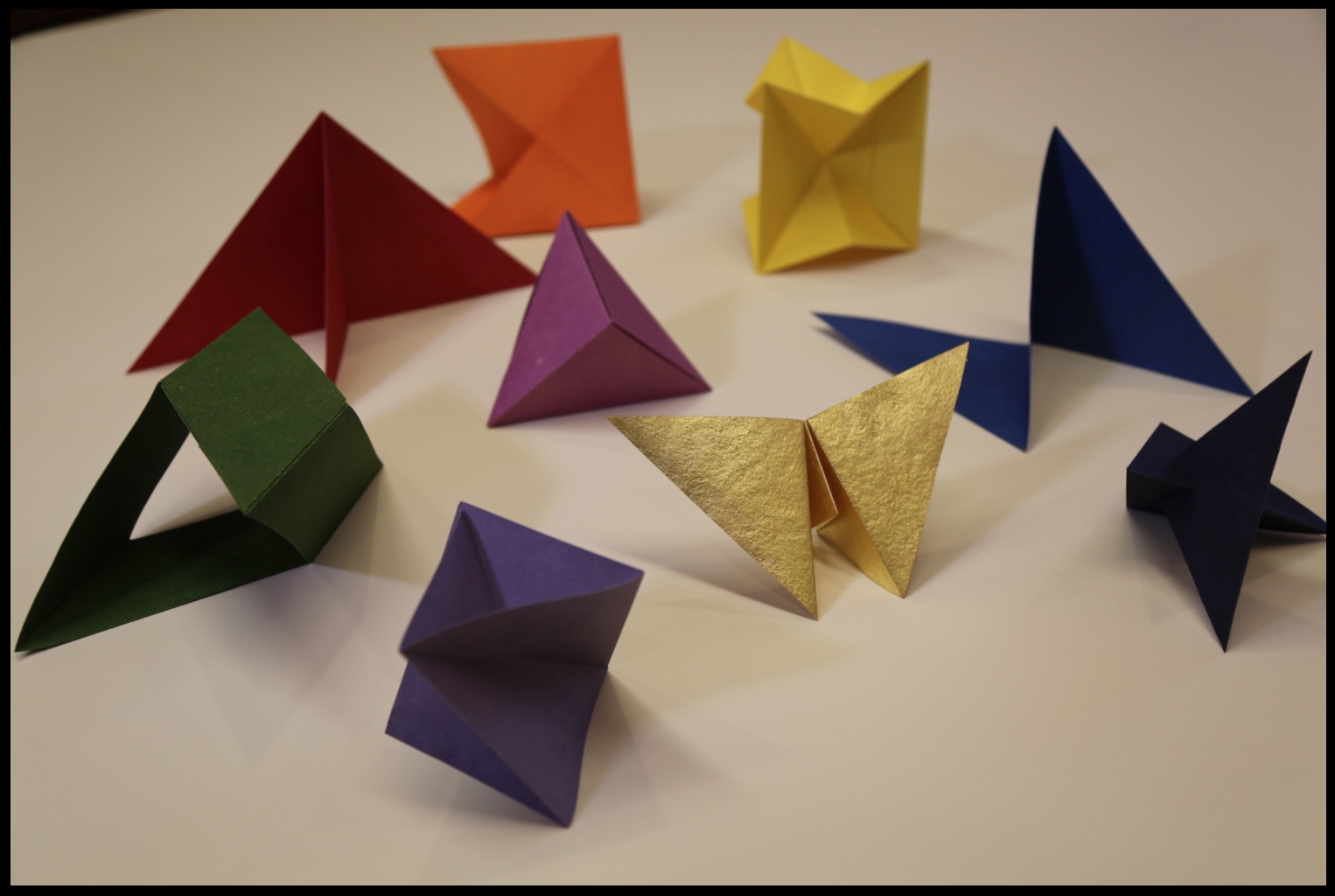
The Art of the Fold‘s clean, balanced design (Alexandre Coco) and excellent diagrams (authors) mesh well with the text. While this integrated clarity in the introductory section on Tools, Materials, Terminology, Symbols and Techniques will be appreciated most by artists and paper engineers, the secondary audience of library/gallery curators, aficionados and collectors will benefit from the description and comments in particular on materials, terminology and techniques. Knowing these points about an object of book art enhances appreciation of it and improves its handling, presentation and preservation.
Following this introduction, Kyle and Warchol provide 36 sets of detailed instructions across 5 sections:
- The Accordion
- Blizzards
- One-Sheet Books
- Albums
- Enclosures

This double-page spread introducing the accordion structure shows off the the diagrams’ clarity, a feature throughout the book. Also in this spread are two important statements in the verso page’s final paragraph:
The accordion fold as an independent component is our focus point in this book…. Let us start with a brief visual display of a variety of folding styles. Hopefully they will inspire you to grab some paper and start folding. (p .28)
The focus on structure “as an independent component” is a strength and weakness. The strength is self-evident in the thoroughness and attention to detail. The weakness? More than occasionally, the authors make asides about the meaningful interaction of structure with content and, occasionally, with other components (type, color, printing technique, etc.). Some exemplars selected by the authors would have been welcome. The artist’s and reader’s challenge is to provide their own examples of how the structural component might work with different types of content, mixed media and other components that combine to deliver the artistic object.
The second statement — the exhortation “to grab some paper and start folding” — illustrates an unalloyed strength of this book. As towering an authority and figure in the book arts and book art as Hedi Kyle is, she and her co-author go out of their way again and again to keep readers open to playing with the techniques and structures and finding their own inventiveness and creativity. For those content to collect or curate, both statements push them to look for or revisit outstanding examples and inventive variants of the structures elucidated. After this section, a browse of Stephen Perkins’ accordion publications, a site running since 2010, would be a good start.

This double-page spread introducing the section on Blizzard structures delivers that blend of the anecdotal with essential engineering-like detail that is characteristic of the authors’ style throughout. Having explained how this family of folded structures that bind themselves got its name (a fold discovered in a daylong fold-a-thon due to a blizzard’s shutting everything down), the authors dive into the proportionality so key to getting them right. Perhaps because of its non-adhesive, origami-centric nature, the blizzard book structure generates more than its fair share of kitsch exemplars. When blizzard books do come along that rise to the level of art — integrating structure, content, printing, typography, color and other components of bookmaking in an artistically meaningful way — they stand out all the more. One such work took first place in the 23 Sandy Gallery’s juried exhibition in 2015, “Hello Hedi”:

Blizzard Book (2015)
Virginia Phelps

Next to The Accordion section, the One-Sheet Books section has the most models. It is also the section that most addresses that challenge mentioned above:
A book folded from a single sheet of paper, including covers, offers a unique opportunity to consider the content and cover as one comprehensive design exercise. We explore the coming together of printing, layout and folding. (P. 94)
Given this opportunity, some treatment of imposition would have been useful, especially for the Franklin Fold and the Booklet Fold Variations. For the Booklet Fold Variations, one could lightly pencil into the book’s clear diagrams the usual markings and enumerations as below.

Again, a few selected photographs of examples of One-Sheet Books that achieve the coming together of content, design, printing, layout and folding would have been welcome.

The double-page spread above with which the Albums section begins exemplifies the book’s quality of photography (by Paul Warchol, Ulla’s husband). Like the “dust jacket”, the crisply photographed Panorama Book structure (upper right) and the pages that explain it will send readers on a quest to make their own or hunt for outstanding examples such as these by Cathryn Miller and Cor Aerssens, a long-time friend and correspondent with Kyle.

Westron Wynde (2016)
Cathryn Miller
Author’s statement: “This book presents the poem ‘Westron Wynde’ in a purely visual form. Letters become colours, and are used as graphic elements. The book manifests the essence, if not the sense, of the poem.”
Westron wynde when wyll thou blow,
The smalle rayne down can rayne –
Cryst, yf my love wer in my armys
And I yn my bed agayne!

Memories (2012)
Cor Aerssens

Memories (2012)
Cor Aerssens

Memories (2012)
Cor Aerssens
A cautionary, or perhaps encouraging, note though: the fact that some structures can enfold others will frustrate readers with strict classificatory minds and exhilarate the more freewheeling. The Phelps’ Blizzard Book highlighted above includes in its sections items exemplifying the Flag Book and Fishbone structures. Aerssens’ Memories is even more so an integrated variant of the Panorama Book structure, featuring as it does panels within panels, two 8-leaf booklets bound into front and back with paper hinges, and mylar folders holding pressed flora from Aerssen’s northern Dutch environs.

The Enclosures section presents fascinating structures, not all of which are suited “to fit many of the projects in the previous chapters”. For example, the second-most fascinating form — the Telescoping Ziggurat, shown in the lower left corner of the recto page above — looks incapable of enclosing any of the other 35 structures. The authors acknowledge it is “less of a book and more of a toy — a stimulating and curious object whose inherent mathematical quality mesmerizes as it spirals inward and outward”. The most fascinating form, however, is as much a book as stimulating and curious object: the Sling Fold structure.


This structure looks suited to enclosing scrolls or narrow, collapsed accordion books of diminishing height, and its mechanics invite playful integration with content and variations of color, typography or calligraphy, printing method and materials.
It would not do to conclude a review of this book without touching on the Flag Book structure, for which Kyle is so well-known. It is found in The Accordion section. The outstanding works implementing this structure are legion. Here it is below in all its glory, which is exceeded only by the Two-Sided Flag book in the pages following it.

The Art of the Fold should become an instant classic. If readers are tempted to “grangerize” their copies with photos and clippings of favorite examples and variants, they would do well instead to create one of the authors’ album structures in which to keep them. There could be many editions of this classic to come.
Update: for more on Kyle and Warchol, see their interview with Helen Hiebert in her series Paper Talk.
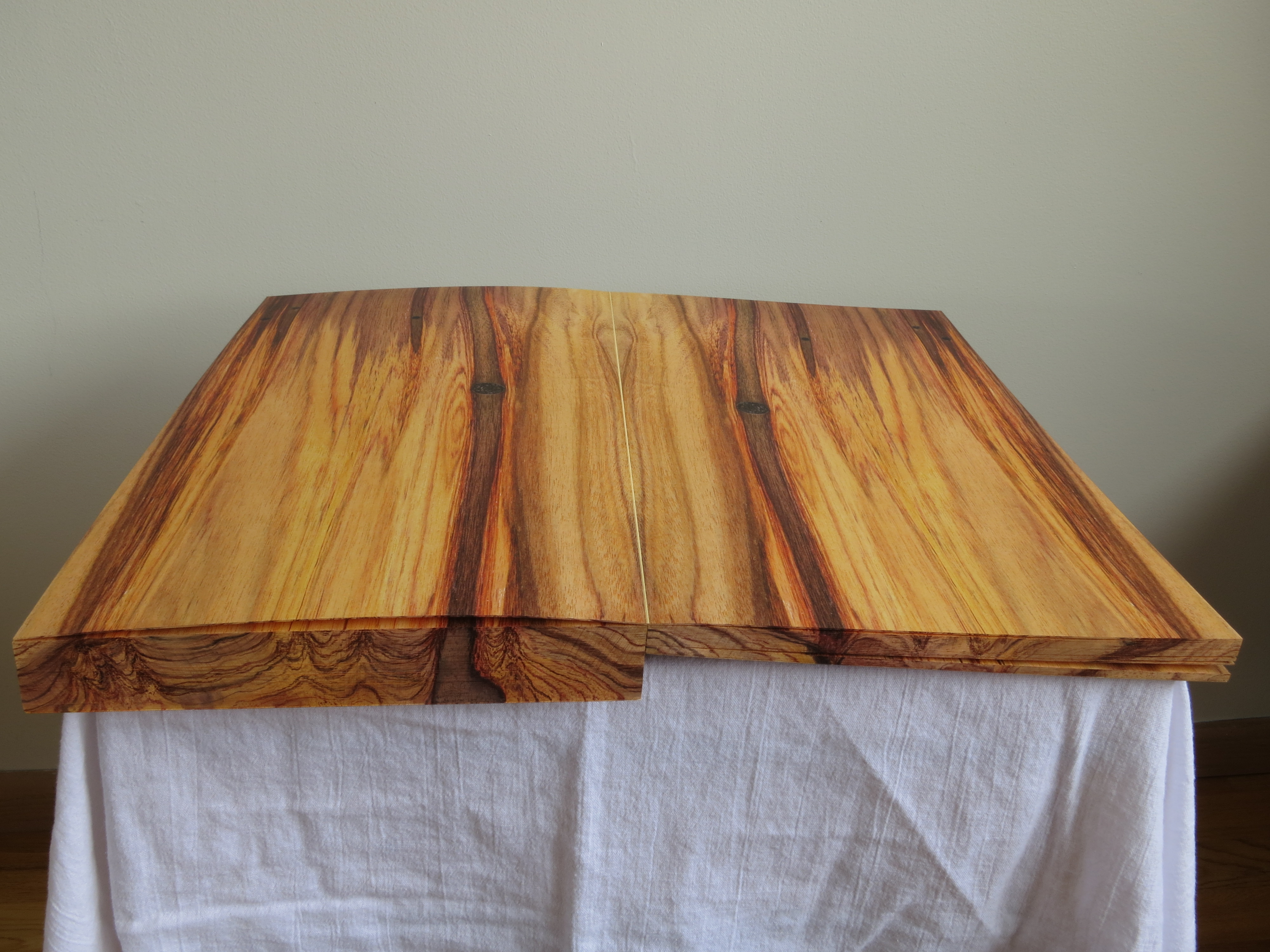
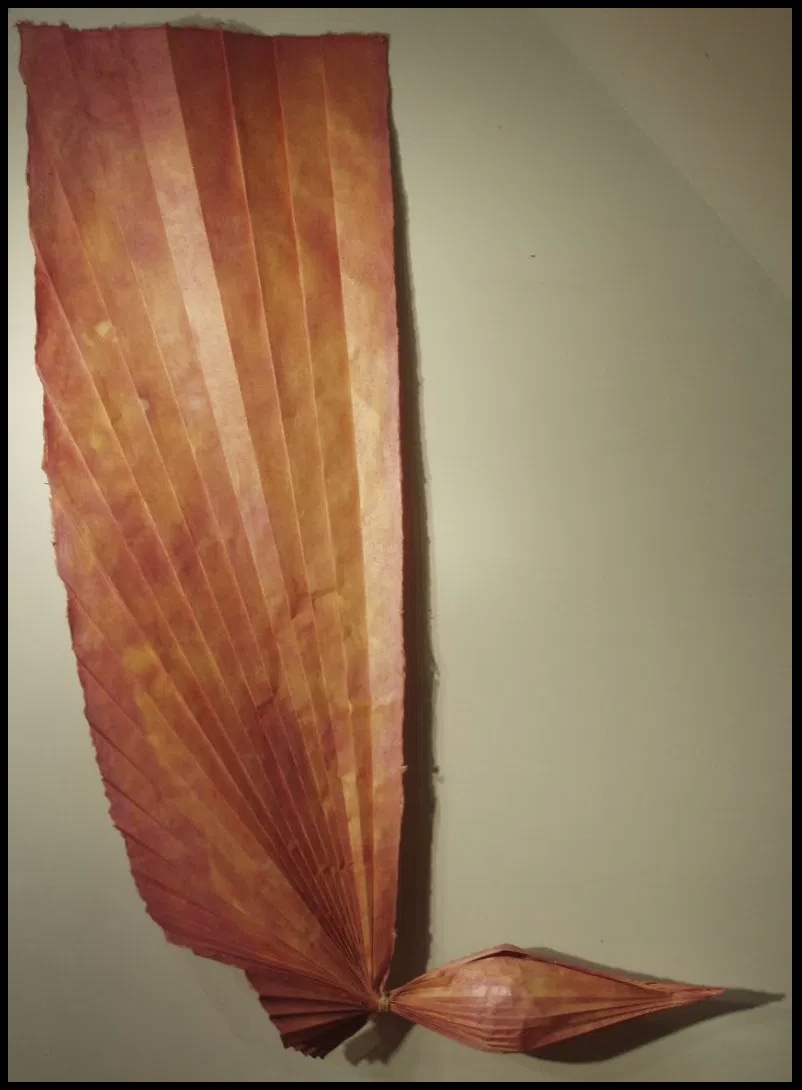
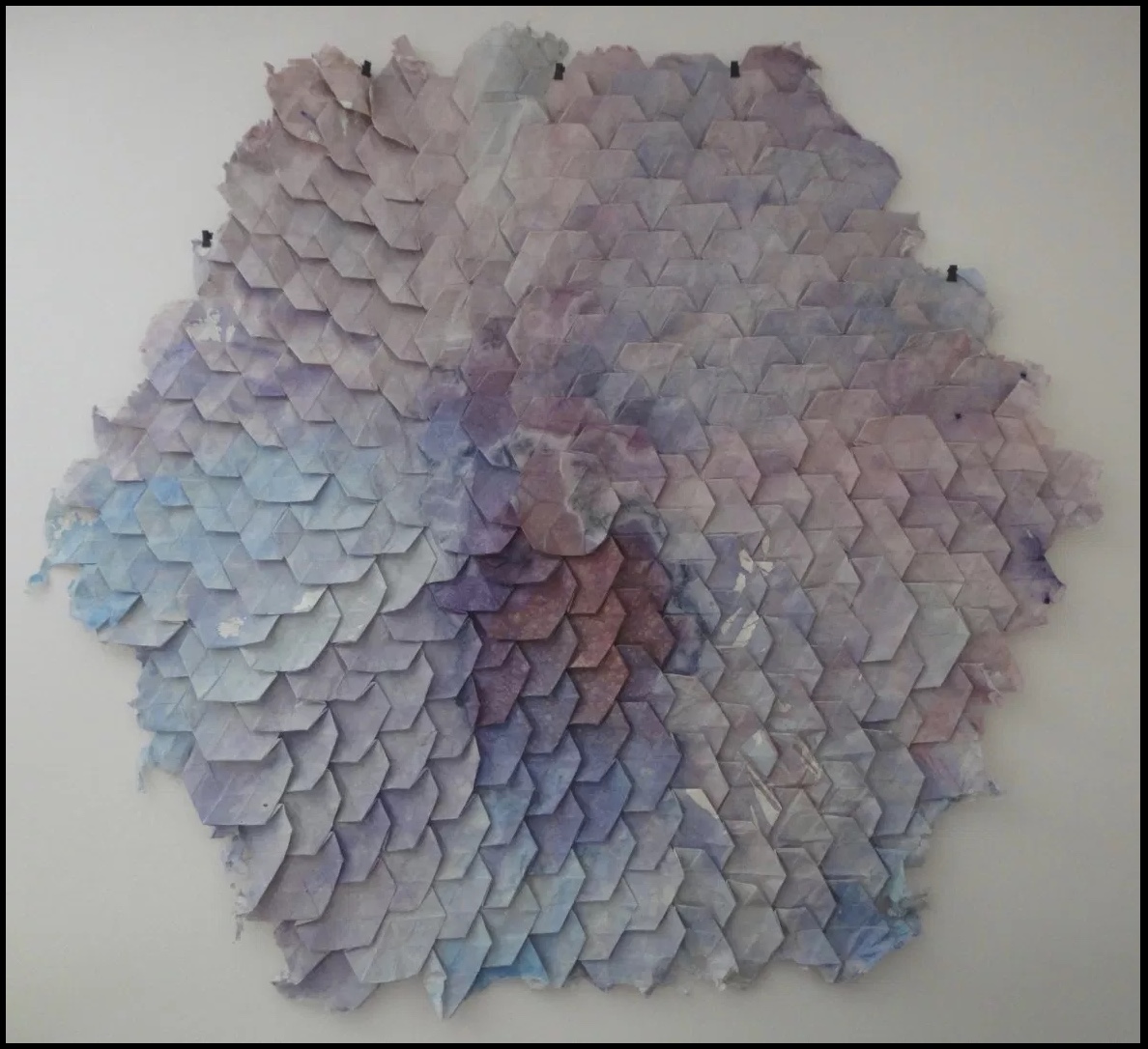
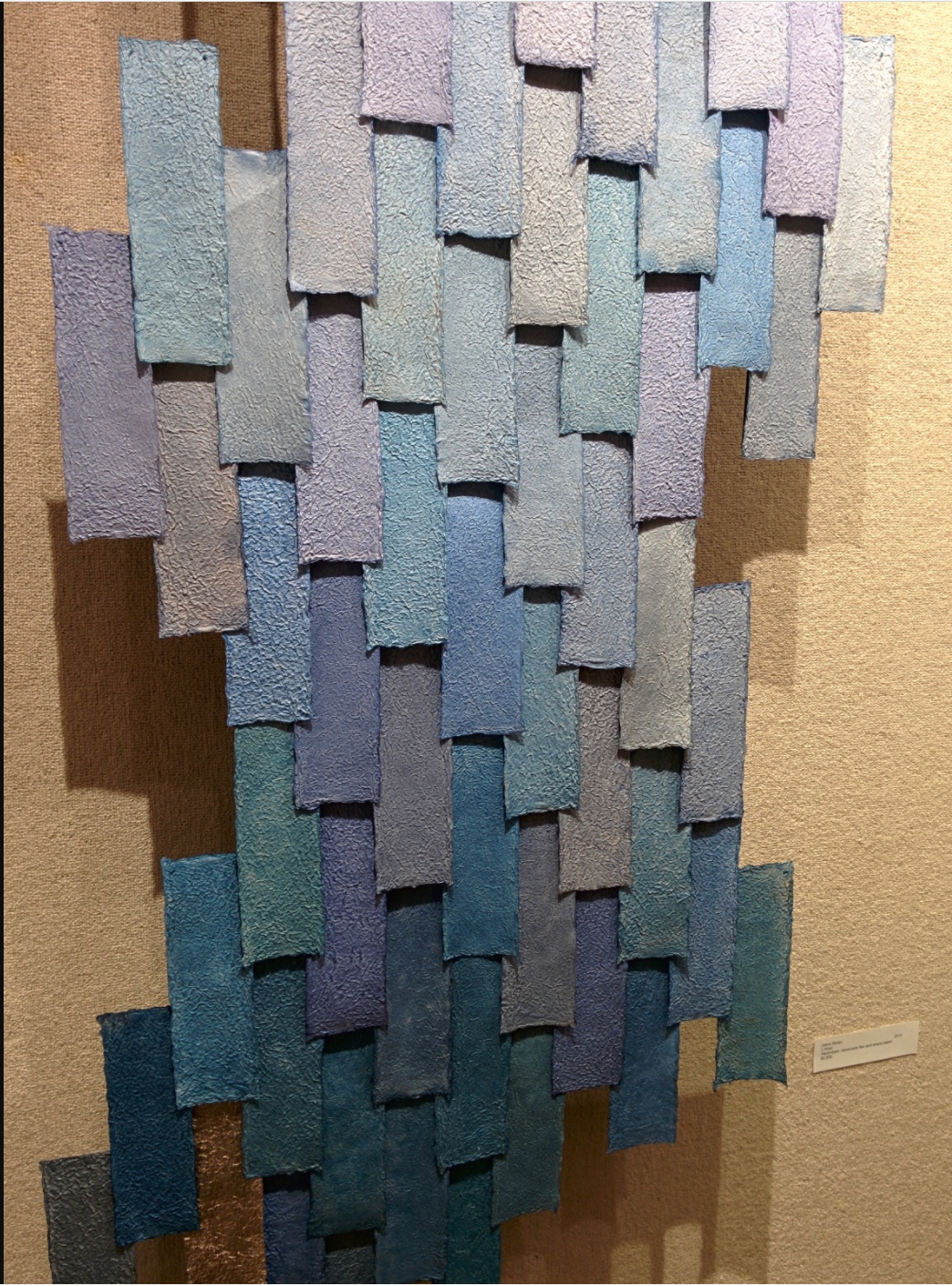























































































































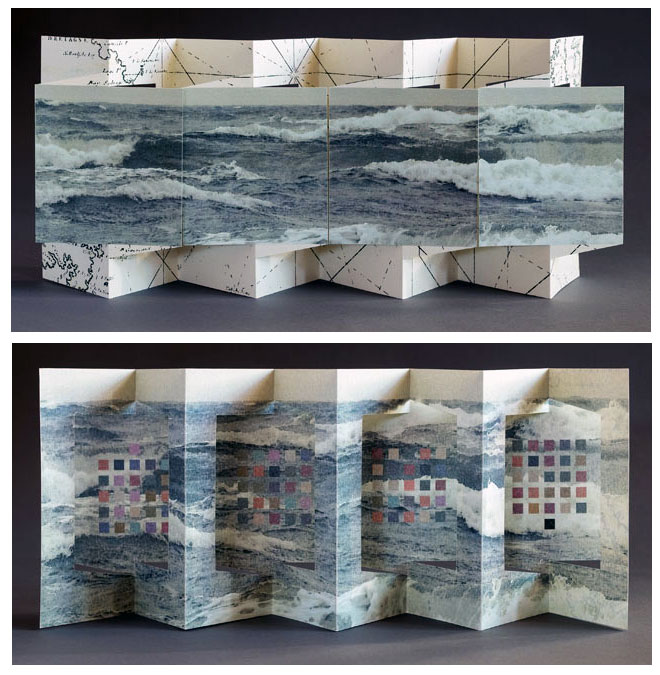
 Consider Schilling’s Half-Life/Full-Life and its binding a variation on the accordion/flag structure of Hedi Kyle and Claire Van Vliet. The complexity of the form marries well with that of the intertwining, interleaving text and photos along the timelines of the Doomsday Clock and global warming.
Consider Schilling’s Half-Life/Full-Life and its binding a variation on the accordion/flag structure of Hedi Kyle and Claire Van Vliet. The complexity of the form marries well with that of the intertwining, interleaving text and photos along the timelines of the Doomsday Clock and global warming.